

KeywordPlasma, MHD, Simulation, Magnetic nozzle, Laser fusion
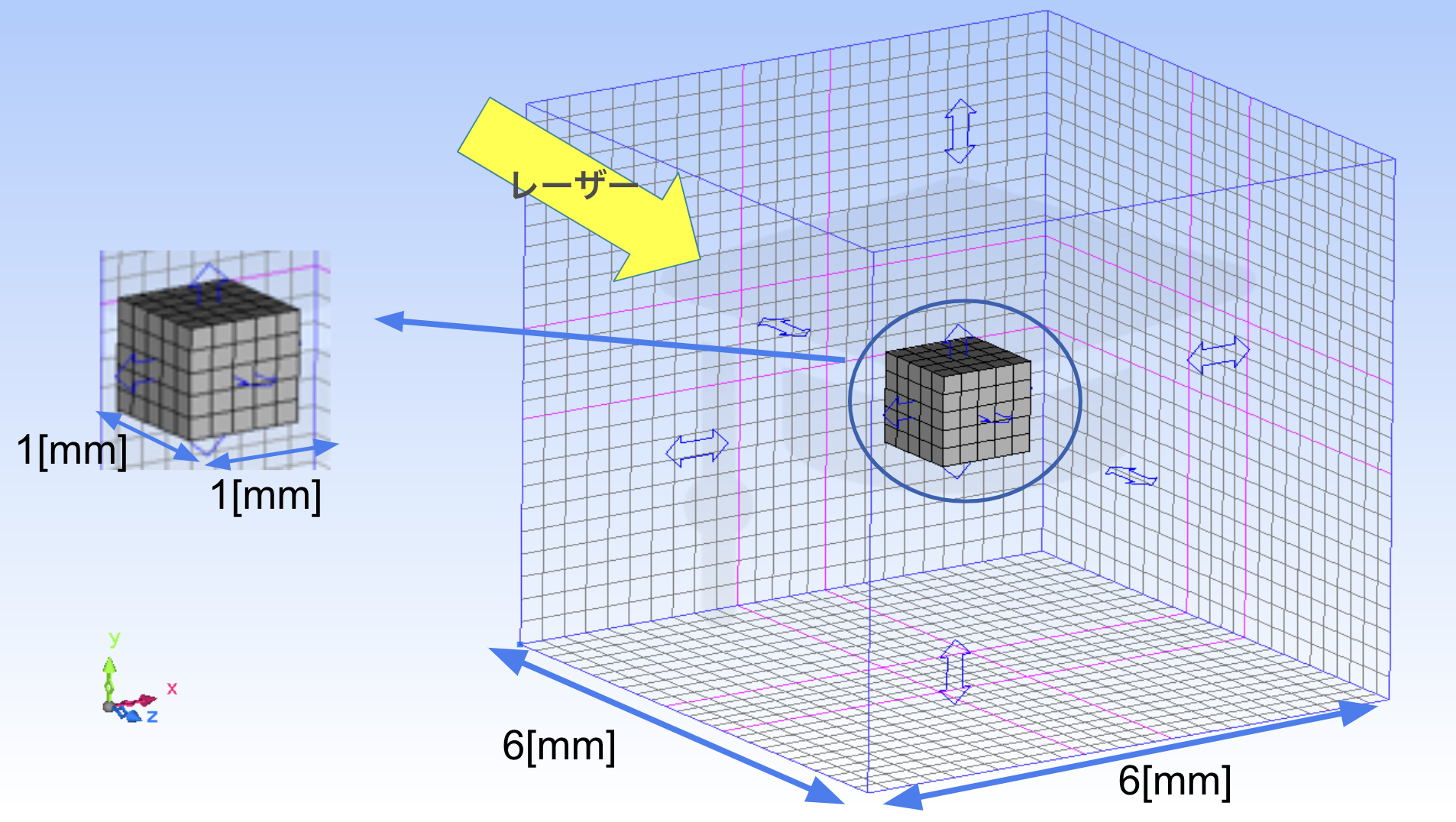
将来の深宇宙飛行に向けたレーザー核融合ロケットの開発において、アブレーションプラズマの磁気ノズル制御技術は推力性能に直接影響を与える重要な要素である。しかし、これまでの研究では、大規模な実験や詳細な数値シミュレーションを実施するためのリソースや技術的な制約が大きく、十分な解析が行われていない状況にある。そこで、本研究ではまず、簡易シミュレーションを用いて、アブレーションプラズマの磁気ノズル内での挙動を解析し、推力の向上に繋がる制御法を模索することを目的としている。
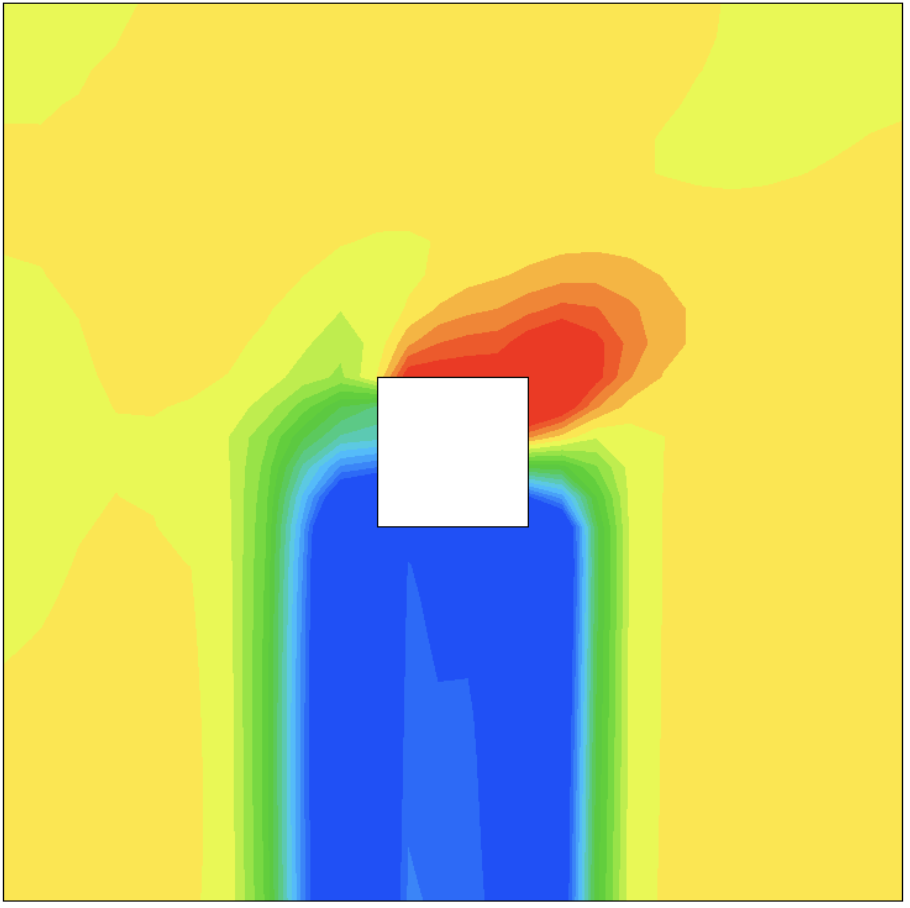
現在、磁束密度をx軸、y軸、z軸それぞれで変化させ、軸方向推力に対するプラズマ流の影響を解析している段階にあり、特定の条件下で軸方向推力が増加する可能性が示唆されつつある。しかし、得られたデータの精度や再現性を高めるためには、さらなる解析が必要であり、実際の最適化は今後の作業として予定している。最適化には、遺伝的アルゴリズムなどの進化的手法を適用することで、複雑なパラメータ空間を効率的に探索し、磁束密度の最適な設定を見出すことを目指している。
現時点では、シミュレーション結果の初期解析が進行中であり、これから最適化アルゴリズムを適用していく段階にある。今後の研究では、さらに精密なシミュレーションを行い、より実用的な推力向上技術の確立を目指して解析を進める予定である。
In the development of laser fusion rockets for future deep space missions, magnetic nozzle control of ablation plasma is a critical factor that directly affects thrust performance. However, previous studies have faced significant technical and resource limitations, making it difficult to conduct large-scale experiments and detailed numerical simulations. As a result, comprehensive analysis has not yet been achieved. This research aims to first analyze the behavior of ablation plasma in a magnetic nozzle using simplified simulations to explore control methods that could lead to improved thrust performance.
Currently, we are in the process of analyzing how changes in magnetic flux density along the x, y, and z axes affect the plasma flow and its contribution to axial thrust. Early indications suggest the potential for an increase in axial thrust under certain conditions. However, further analysis is required to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of the data, and the actual optimization process is planned for the next phase. In this optimization, evolutionary methods such as genetic algorithms will be applied to efficiently explore the complex parameter space and identify the optimal magnetic flux density settings.
At this stage, initial analysis of the simulation results is underway, and the optimization algorithms will be applied moving forward. Future work will involve conducting more precise simulations to establish practical thrust enhancement techniques as the research progresses.